Onboard inference¶
Goal¶
This tutorial shows how to run ground segmentation on Leopard using previously prepared model and Deep learning Processor Unit accelerator.
A bit of background¶
Running inference requires building Linux distribution with DPU support, prepared model, runner script and input data. You’ve already prepared all these components in different tutorials, this one puts everything together. Runner in this tutorial will perform ground segmentation and output numeric predictions results for each input image along with visualization of segmentation by overlying classes on top of input images.
Prerequisites¶
Yocto project with Deep learning Processor Unit (Deep-learning Processor Unit)
Quantized model (Model compilation)
Python tool for running inference (Onboard model runner in Python)
3-4 test images from ML dataset in form of 512x512 patches (Tutorial files)
Provided outputs¶
Following files (Tutorial files) are associated with this tutorial:
Leopard/Zero-to-hero/05 Onboard inference/boot-common.bin- Boot firmware for LeopardLeopard/Zero-to-hero/05 Onboard inference/nominal-image-leopard-dpu.rootfs.cpio.gz.u-boot- Root filesystem for LeopardLeopard/Zero-to-hero/05 Onboard inference/Image- Linux kernelLeopard/Zero-to-hero/05 Onboard inference/system.dtb- Device tree
Use these files if you don’t want to build Yocto distribution by yourself.
Add inference tools to Yocto project Yocto¶
Note
If necessary, re-enable Yocto environment using
machine:~/leopard-linux-1$ source sources/poky/oe-init-build-env ./build
Create directory
~/leopard-linux-1/sources/meta-local/recipes-example/inference/inference/Copy
model_runner.pyto~/leopard-linux-1/sources/meta-local/recipes-example/inference/inference/Copy
deep_globe_segmentation_unet_512_512.xmodelto~/leopard-linux-1/sources/meta-local/recipes-example/inference/inference/Create new recipe
~/leopard-linux-1/sources/meta-local/recipes-example/inference/inference.bbLICENSE = "CLOSED" SRC_URI = "\ file://model_runner.py \ file://deep_globe_segmentation_unet_512_512.xmodel \ " RDEPENDS:${PN} = "\ python3-opencv \ xir \ vart \ " do_install() { install -d ${D}/dpu-inference install -m 0644 ${WORKDIR}/model_runner.py ${D}/dpu-inference install -m 0644 ${WORKDIR}/deep_globe_segmentation_unet_512_512.xmodel ${D}/dpu-inference } FILES:${PN} += "/dpu-inference/*"Add new packages into Linux image by editing
~/leopard-linux-1/sources/meta-local/recipes-leopard/images/nominal-image.bbappendIMAGE_INSTALL += "\ fpga-manager-script \ double-uart \ dpu \ vitis-ai-library \ kernel-module-xlnx-dpu \ inference \ "Build firmware and image
machine:~/leopard-linux-1/build$ bitbake leopard-allPrepare build artifacts for transfer to EGSE Host
machine:~/leopard-linux-1/build$ mkdir -p ../egse-host-transfer machine:~/leopard-linux-1/build$ cp tmp/deploy/images/leopard-dpu/bootbins/boot-common.bin ../egse-host-transfer machine:~/leopard-linux-1/build$ cp tmp/deploy/images/leopard-dpu/system.dtb ../egse-host-transfer machine:~/leopard-linux-1/build$ cp tmp/deploy/images/leopard-dpu/nominal-image-leopard-dpu.rootfs.cpio.gz.u-boot ../egse-host-transfer machine:~/leopard-linux-1/build$ cp tmp/deploy/images/leopard-dpu/Image ../egse-host-transferTransfer content of
egse-host-transferdirectory to EGSE Host and place it in/var/tftp/tutorialdirectory
Run inference on DPU EGSE Host¶
Upload few images from DeepGlobe dataset (Tutorial files) to run inference on to EGSE Host and place them in
~/inference-inputdirectory. Use patched files (512x512).Verify that all necessary artifacts are present on EGSE Host:
customer@egse-host:~$ ls -lh /var/tftp/tutorial total 134M -rw-rw-r-- 1 customer customer 21M Jul 16 11:15 Image -rw-rw-r-- 1 customer customer 1.6M Jul 16 11:15 boot-common.bin -rw-rw-r-- 1 customer customer 121M Jul 16 11:15 nominal-image-leopard-dpu.rootfs.cpio.gz.u-boot -rw-rw-r-- 1 customer customer 39K Jul 16 11:15 system.dtb customer@egse-host:~$ ls -lh ~/inference-input total 225K -rw-rw-r-- 1 customer customer 71K Jan 30 07:58 207743_04_02_sat.jpg -rw-rw-r-- 1 customer customer 77K Jan 30 07:58 207743_04_03_sat.jpg -rw-rw-r-- 1 customer customer 76K Jan 30 07:58 21717_04_02_sat.jpgNote
Exact file size might differ a bit but they should be in the same range (for example
nominal-image-leopard-dpu.rootfs.cpio.gz.u-bootshall be about ~120MB)Note
You can choose different images to run inference on.
Ensure that Leopard is powered off
customer@egse-host:~$ sml power off Powering off...SuccessOpen second SSH connection to EGSE Host and start
minicomto observe boot processcustomer@egse-host:~$ minicom -D /dev/sml/leopard-pn1-uartLeave this terminal open and get back to SSH connection used in previous steps.
Power on Leopard
customer@egse-host:~$ sml power on Powering on...SuccessPower on DPU Processing Node 1
customer@egse-host:~$ sml pn1 power on --nor-memory nor1 Powering on processing node Node1...SuccessNote
Boot firmware is the same as in Enable programmable logic support.
DPU boot process should be visible in
minicomterminalTransfer images from EGSE Host to Processing Node
customer@egse-host:~$ scp -r ~/inference-input pn1:/tmp/inference-input Warning: Permanently added '172.20.200.100' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts. 21717_04_02_sat.jpg 100% 76KB 16.1MB/s 00:00 207743_04_03_sat.jpg 100% 77KB 27.1MB/s 00:00 207743_04_02_sat.jpg 100% 70KB 29.4MB/s 00:00Log in to DPU using
rootuserleopard login: root root@leopard:~#Load DPU bitstream
root@leopard:~# fpgautil -o /lib/firmware/dpu/overlay.dtboRun inference. Runner creates output directory automatically.
root@leopard-dpu:~# python3 /dpu-inference/model_runner.py \ --input-dir /tmp/inference-input/ \ --output-dir /tmp/inference-output Input tensors shape: [[1, 512, 512, 3]] Output tensors shape: [[1, 512, 512, 7]] Input tensors dtype: ['xint8'] Output tensors dtype: ['xint8'] Processing image /tmp/inference-input/21717_04_02_sat.jpg Infering... /dpu-inference/model_runner.py:24: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in exp return np.exp(image) / np.sum(np.exp(image), axis=classes_axis, keepdims=True) /dpu-inference/model_runner.py:24: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide return np.exp(image) / np.sum(np.exp(image), axis=classes_axis, keepdims=True) Rendering... Processing image /tmp/inference-input/207743_04_03_sat.jpg Infering... Rendering... Processing image /tmp/inference-input/207743_04_02_sat.jpg Infering... Rendering...Note
You can ignore “overflow encountered in exp” warning.
Verify that
model_runner.pyproduced resultsroot@leopard-dpu:~# ls -l /tmp/inference-output/ -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 73077 Jan 30 08:17 207743_04_02_sat.jpg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7340160 Jan 30 08:17 207743_04_02_sat.npy -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 78363 Jan 30 08:17 207743_04_03_sat.jpg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7340160 Jan 30 08:17 207743_04_03_sat.npy -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 77827 Jan 30 08:17 21717_04_02_sat.jpg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7340160 Jan 30 08:17 21717_04_02_sat.npyScript has produced
.npyand.jpgfiles for each input image.Transfer inference results back to EGSE Host
customer@egse-host:~$ scp -r pn1:/tmp/inference-output/* /var/www/html/inference-output Warning: Permanently added '172.20.200.100' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts. 207743_04_02_sat.jpg 100% 71KB 16.2MB/s 00:00 207743_04_02_sat.npy 100% 7168KB 53.3MB/s 00:00 207743_04_03_sat.jpg 100% 77KB 32.7MB/s 00:00 207743_04_03_sat.npy 100% 7168KB 53.4MB/s 00:00 21717_04_02_sat.jpg 100% 76KB 32.9MB/s 00:00 21717_04_02_sat.npy 100% 7168KB 53.4MB/s 00:00Open
http://egse-<id>.egse.vpn.sml.kplabs.space/inference-outputin your Web browser and review rendered images.
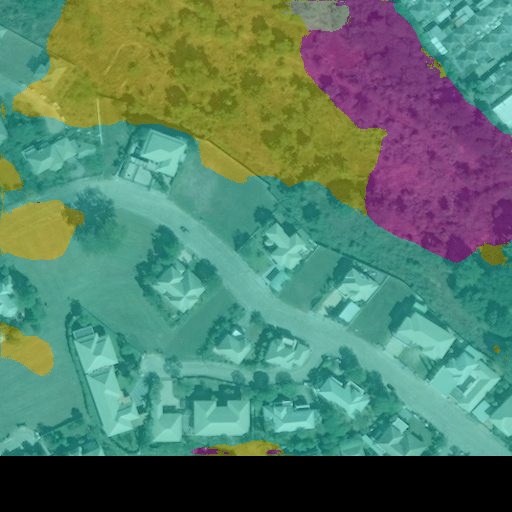
Fig. 12 21717_04_02_sat.jpg¶ |
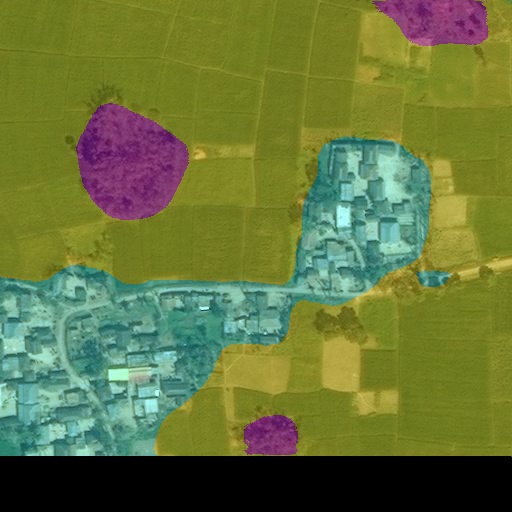
Fig. 13 207743_04_02_sat.jpg¶ |
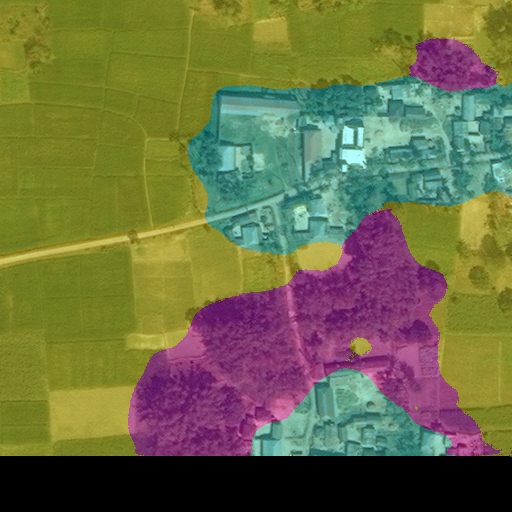
Fig. 14 207743_04_03_sat.jpg¶ |

Fig. 15 Legend¶ |
Summary¶
In this tutorial you’ve put together all pieces created in Zero to hero tutorial series. Using DPU accelerator and small Python script you’ve managed to run ground segmentation on series of images. That involved trained, quantized and compiled model for specific architecture, Linux distribution with DPU support and Python script to run inference. You can use inference results to generate images or other processing.